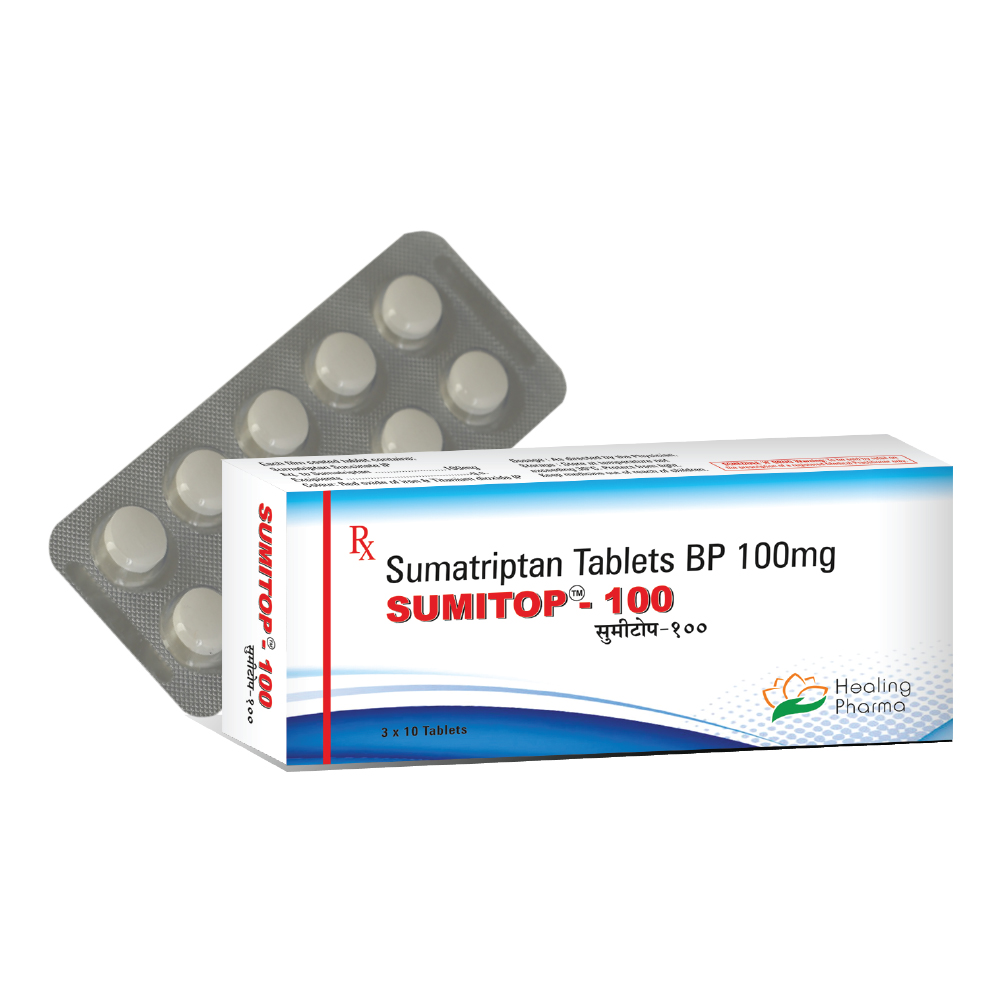
Sumitrex
Brand names: Sumitrex, Sumitop, Imigran, Imitrex
Generic name: Sumatriptan
Manufacturer: Healing Pharma
How does Sumatriptan work?
Sumitrex tablets and contain the active ingredient sumatriptan, which is a type of medicine called a serotonin (or 5HT) agonist. This type of medicine is also commonly known as a ‘triptan’. It is a painkiller specifically used to relieve migraine attacks. (NB. Sumatriptan is also available without a brand name, ie as the generic medicine.)
Although the cause of migraine attacks is not fully understood, it is thought that widening of blood vessels in the brain causes the throbbing pain of migraine headaches. Sumatriptan relieves this pain by causing the blood vessels in the brain to narrow.
Sumatriptan works by stimulating receptors called serotonin (or 5HT) receptors that are found in the brain. A natural substance called serotonin normally acts on these receptors, causing blood vessels in the brain to narrow. Sumatriptan mimics this action of serotonin by directly stimulating the serotonin receptors in the brain. This narrows the blood vessels and so relieves the pain of migraine headaches.
The dose of sumatriptan should be taken as early as possible after the migraine headache has started, though it is also effective if taken at a later stage during the migraine attack.
During a migraine attack, the normal movements of the stomach can slow down or stop. This can delay tablets from dissolving in the stomach and the medicine being absorbed into the bloodstream. Imigran Radis tablets are designed to disintegrate in the stomach more rapidly than standard Imigran tablets, which means they may start to work faster than the standard tablets.
What is Sumitrex used for?
Relieving migraine attacks.
Warning!
• This medicine should not be used to prevent migraines.
• This medicine should only be used by people with a clear diagnosis of migraine from their doctor.
• If the first dose of this medicine doesn’t relieve your migraine headache then you should NOT take another dose for the same attack, as trials have shown that this is not effective. (You can still take Imigran for your next attack.) If your first dose does initially relieve your migraine, but the headache then comes back, you can take a second dose. However, if you need a second dose because your migraine has returned, you should NOT take it within two hours of your first dose. Do not exceed the recommended dose. Do not take more than 300mg in any 24 hour period.
• Consult your doctor if your migraine doesn’t go away, or if you have frequent or daily migraines. It is important not to use this medicine too frequently, because taking a painkiller for headaches or migraines too often or for too long can actually make the headaches worse.
• This medicine can cause feelings of warmth, heaviness, pressure, tightness or pain in certain parts of the body, including the chest or throat. Although sometimes very strong, these feelings usually only last a few minutes. If they continue or are particularly severe (especially chest pain), you should tell your doctor immediately, as there have been extremely rare reports of such problems being caused by a heart attack. Do NOT take any more tablets; your doctor will decide if you should stop using them.
• This medicine may cause drowsiness. If affected do not drive or operate machinery.
Use with caution in
• Allergy to medicines from the sulphonamide group, eg the antibiotic sulfamethoxazole.
• Controlled high blood pressure (hypertension).
• People with risk factors for ischaemic heart disease, such as smoking, high cholesterol levels, diabetes, obesity, or a family history of heart disease.
• Men over 40 years.
• Postmenopausal women.
• Decreased kidney function.
• Decreased liver function.
• History of seizures eg epilepsy, or people with conditions that increase the risk of seizures, eg head injury, alcoholism.
Not to be used in
• People who have had a heart attack.
• Heart disease caused by inadequate blood flow to the heart (ischaemic heart disease), eg angina.
• A severe form of angina pectoris, not caused by exertion (Prinzmetal’s angina).
• Narrowing of blood vessels in the extremities, eg legs (peripheral vascular disease).
• History of stroke.
• History of small temporary temporary strokes (transient ischaemic attacks).
• Uncontrolled or moderate to severe high blood pressure (hypertension).
• Severely decreased liver function.
• People who have taken a monoamine-oxidase inhibitor antidepressant (MAOI) in the last 14 days.
• A form of migraine associated with paralysis of the eye muscles (ophthalmoplegic migraine).
• A form of migraine associated with temporary paralysis of one side of the body (hemiplegic migraine).
• A type of migraine where there is a disturbance in brain function which initially presents with total blindness followed by dizziness, speach disturbances, ringing in the ears and double vision (basilar migraine).
Sumitrex tablets are not recommended for children or adolescents aged under 18 years, or adults aged over 65 years, as the safety and efficacy of the tablets have not been established in these age groups. Adolescents aged 12-17 years can be treated with Imigran nasal spray, but only on the recommendation of a specialist or doctor with particular experience in migraine. See the factsheet on Imigran nasal spray (linked at the end of this page) for more information.
- Sumitrex tablets contain lactose and should not be taken by people with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, the Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption.
This medicine should not be used if you are allergic to one or any of its ingredients. Please inform your doctor or pharmacist if you have previously experienced such an allergy.If you feel you have experienced an allergic reaction, stop using this medicine and inform your doctor or pharmacist immediately.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Certain medicines should not be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding. However, other medicines may be safely used in pregnancy or breastfeeding providing the benefits to the mother outweigh the risks to the unborn baby. Always inform your doctor if you are pregnant or planning a pregnancy, before using any medicine.
- The safety of this medicine during pregnancy has not been established. It should only be used by pregnant women if the expected benefit to the mother is greater than any possible risk to the developing baby. Seek medical advice from your doctor.
- This medicine passes into breast milk. It should be used with caution by breastfeeding mothers. Exposure of the baby to the medicine can be minimised by not breastfeeding for 12 hours after you have taken a dose. Discard any breast milk you express in this time. Seek further medical advice from your doctor.
Side effects
Medicines and their possible side effects can affect individual people in different ways. The following are some of the side effects that are known to be associated with this medicine. Just because a side effect is stated here does not mean that all people using this medicine will experience that or any side effect.
Common (affect between 1 in 10 and 1 in 100 people)
Sensation of tightness, pressure, tingling, heaviness, heat or pain in any part of the body, including the chest and throat (see warning above).
Flushing.
Increase in blood pressure.
Shortness of breath.
Dizziness.
Drowsiness.
Weakness.
Fatigue.
Nausea and vomiting (though these may also be due to the migraine).
Very rare (affect less than 1 in 10,000 people)
- Visual disturbances such as flickering, reduced vision, double vision or loss of vision (though these may also be due to the migraine).
- Tremor.
- Seizures.
- Stiff neck.
- Increased or decreased heart rate (tachycardia or bradycardia).
- Awareness of your heart beat (palpitations).
- Irregular heart beats.
- Chest pain
- Heart attack.
- Alteration in results of liver function tests.
- Narrowing of the blood vessels in the hands leading to periods of white, painful hands (Raynaud’s phenomenom).
- Low blood pressure (hypotension).
The side effects listed above may not include all of the side effects reported by the medicine’s manufacturer.For more information about any other possible risks associated with this medicine, please read the information provided with the medicine or consult your doctor or pharmacist.
How can this medicine affect other medicines?
It is important to tell your doctor or pharmacist what medicines you are already taking, including those bought without a prescription and herbal medicines, before you start treatment with this medicine. Similarly, check with your doctor or pharmacist before taking any new medicines while taking this one, to ensure that the combination is safe.
This medicine must not be taken at the same time as, or within two weeks of, taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), for example, the antidepressants phenelzine, tranylcypromine, isocarboxazid and moclobemide, and the antibiotic linezolid. This is because these medicines could increase the blood level of sumatriptan and therefore increase the risk of side effects.
This medicine must not be taken in combination with any other triptan medicines, eg zolmitriptan, eletriptan, naratriptan.
This medicine must not taken within 24 hours of taking ergotamine or its derivatives, eg dihydroergotamine or methysergide. These medicines should not be taken within six hours of taking sumatriptan.
If your first dose of sumatriptan does not work to relieve your migraine, it is fine to take a painkiller containing aspirin, paracetamol, or a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), such as ibuprofen. However, as noted above, you should not take ergotamine, dihydroergotamine or methysergide for at least six hours after taking sumatriptan.
There may be an increased risk of a rare side effect called the serotonin syndrome if sumatriptan is taken in combination with other medicines that enhance the activity of serotonin in the central nervous system, such as the following:
- selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants (SSRIs), such as citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine or sertraline
- serotonin noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), such as venlafaxine or duloxetine
- the herbal remedy St John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum).
If you are taking any of these medicines you should let your doctor know if you experience symptoms such as confusion, agitation, tremor, muscle twitching, shivering, sweating, racing heartbeat or diarrhoea after taking sumatriptan.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.